What is Sleep Apnea?
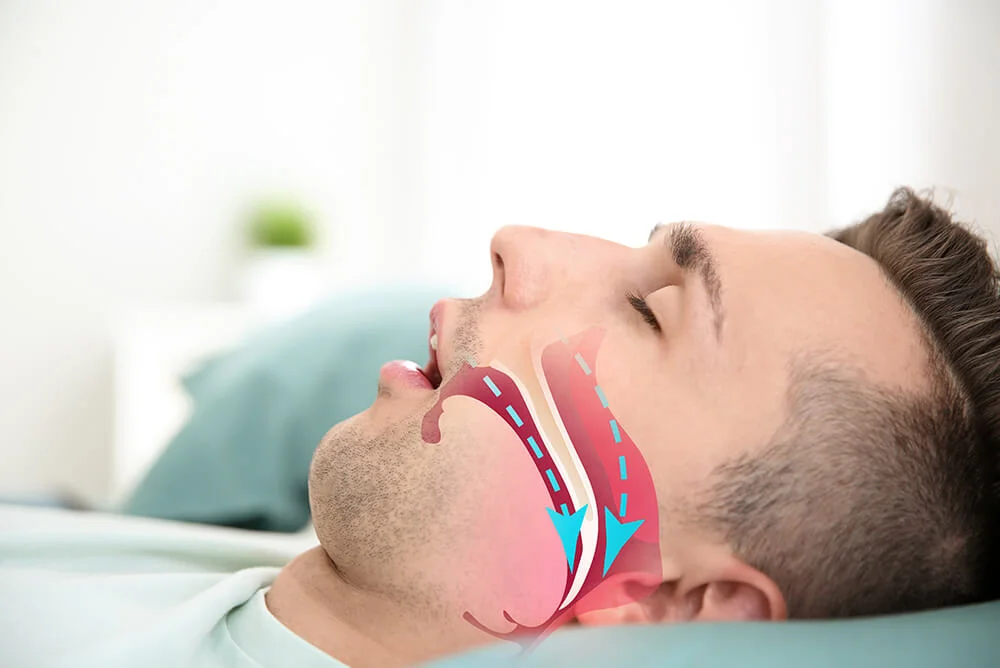
Sleep apnea is a common condition where you have pauses in your breathing (apnea) or excessively shallow breathing (hypopnea) while you sleep.
These pauses can occur as often as five or up to thirty or more times an hour. Normal breathing restarts with a gasping, snorting or choking sound. This results in poor sleep quality or light sleep, causing unrefreshing sleep and daytime drowsiness. It is typically a chronic condition that increases your risk of other medical conditions like high blood pressure and heart disease.
Someone who has sleep apnea may not know they have the condition because they may fall back asleep quickly. Sleep apnea is also not usually detectable during routine doctors’ visits. Often, a bed partner will be the first to notice these episodes of pauses in breathing overnight.
There are three types of sleep apnea:
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) – this is the more common condition, where your throat and airway collapses during sleep, blocking air from reaching your lungs
- Central Sleep Apnea (CSA) – this is a less common condition, where the brain center that controls breathing does not properly send signals to your respiratory muscle, causing pauses in breathing
- Mixed Sleep Apnea – where there is a component of both obstructive sleep apnea and central sleep apnea

